How to calculate speed
Speed is a concept that is essential to life and a prerequisite for many things. It is used in all fields, including hard disciplines such as engineering, medicine, and computing, as well as easier disciplines such as athleticism. With speed, one is able to gauge the speed at which an athlete runs or the speed at which a car can move.
In this article, we will discuss everything related to speed that you may want to know. We will show how to calculate speed, find distance given the speed, and find time given the speed. We will also explain how speed is measured in various units, such as kilometers per hour or meters per second.
We will also explain in easy words how each discussed concept is important for you, including examples, calculations, and formulas.
Well, read on to get more enlightenment on the concept of speed.
In this guide, we’ll cover different types of percentage calculations, including:
- How To Calculate Speed
- How do you calculate speed per km?
- How to calculate distance
- How to calculate time
- How to calculate velocity
- How to calculate acceleration
- How to Calculate Average Speed
- How to Calculate Speed in Circular Motion
- How to Calculate Speed Using GPS
- Instantaneous Speed vs. Average Speed
How To Calculate Speed
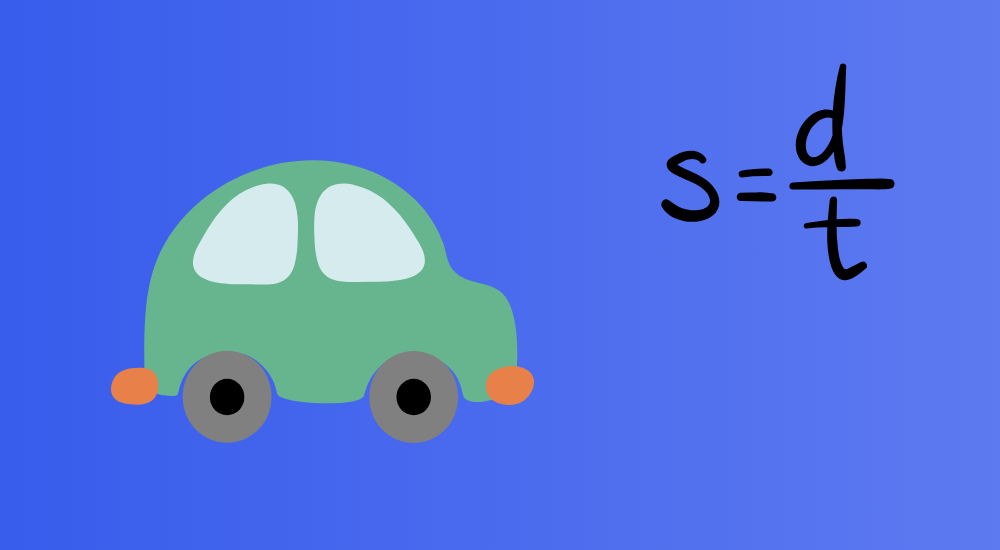
Speed is a measure of how much distance an object travels compared with the amount of time it takes. It is a scalar quantity because it describes only how fast an object is moving. It does not describe the direction of the motion. Contrast this with velocity, which does account for the direction of movement, but more on that later.
Formula
Speed = Distance / Time
There are several units in which you can calculate speed, mainly depending on the units of distance that you will be using. They include :
- Miles per hour (mph): Mainly used in some countries, such as the United States.
- Meters per second (m/s): Usually in scientific use.
- Kilometers per hour (km/h): Common for measuring the speeds of vehicles.
Example
Let’s say you’re driving from point A to point B, which is about 180 kilometers. So, what speed did you drive at if it only took you 3 hours to reach point B? Let’s see!
Step-by-step Calculation:
Speed = 180 km / 3 hrs = 60 km/h
And so, the average speed is 60 kilometers per hour.
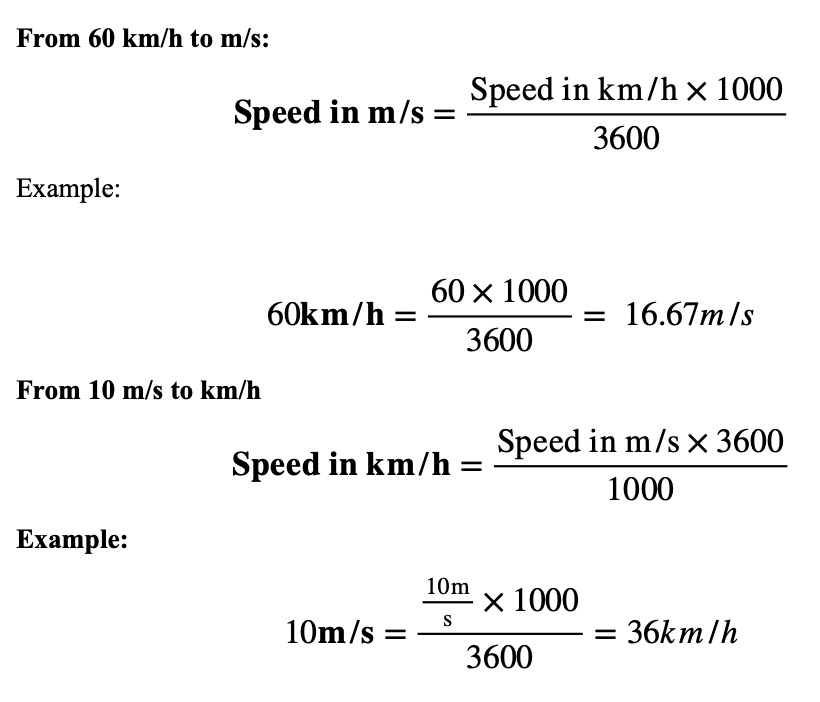
Different Units of Speed
As stated, since it can be expressed in several units, speed is quite a versatile concept. The method of expressing speed will depend on the system of measurement that is to be used at any particular time.
So, if you’ve got speed in one unit, say meters per second, and you want it in kilometers per hour. How do you convert that?
Let us see how speed in different units is converted:
How do you calculate speed per km?
At other times, you may want to know how fast something is moving per one kilometer. When you have speed, you can tell how much time it will take you to move from one point to another.
Suppose, for instance, your driving speed in a car is 45km/hr, and every morning, you must report to work at 8:30 am. With this, you can estimate the distance from home to work and thereby calculate how long it will take for you to drive at 45km/hr to report to work on time.
Formula (for speed per km):
Speed = Distance / Time
In this case, the distance is always in kilometers, and time is majorly in hours. Thus, where the time given is in minutes or seconds, it is always changed into its hours equivalent to make it correspond with the distance in kilometers.
Example:
If it took 45 minutes for a marathon runner to complete a 10-kilometer race, how fast was the runner running?
Well, let’s do a step-by-step calculation.
Step 1: Since time is in minutes, we will need to start by converting the time into hours:
45 mins = 45 / 60 = 0.75 hours
Step 2: Now that we have time in hours, let’s calculate the runner’s average speed:
Speed = 10km / 0.75 hours = 13.33 km/h
Just like that, we can tell how the runner was moving first by using their average speed per kilometer, which is 13.33 km/h.
How to calculate distance
At times, you might happen to have the speed at which a certain object or people were moving and the time taken to cover a certain distance but not the distance itself. In such a situation, you can use speed and time to tell the distance they moved or traveled.
As in the case of speed, other units of showing distance include:
- Meters
- Miles
- Kilometres
Now, note that:
- When the speed is in m/s, you want to have time in seconds.
- Also, when the average speed is in km/h, you want to have time to be in hours, not minutes nor seconds.
Sometimes, you might happen to have the speed at which something or someone was moving and the time it took them to move from one point to another, but no distance. In such a situation, you can utilize speed and time to tell the distance they moved.
The formula for finding distance is:
Distance = Speed x Time
Example:
If it takes you 4 hours to travel from point A to B at a speed of 25km/h, what distance did you actually cover?
Let’s do the calculation:
Step-by-step Calculation:
Distance = 25km/h x 4 hours = 100 kilometers
The cyclist travels 100 kilometers.
Using Distance in Everyday Contexts:
This distance formula is valuable in that it is used in various real-life scenarios, such as:
- Driving
- Sports
- Flight
How to calculate time
This is quite similar to what we have been able to establish with distance, whereby you can also have speed and distance, but you do not know the time taken. With this, you are supposed to make calculations based on the information provided to ascertain how long it took to complete something or to cover a certain distance.
But here are a few things to note:
If speed is in km/h and distance is in meters, then you will need to convert one of these two to relevant units. For example, if you’re required to determine time in hours, then you need to convert meters into km. However, if you’re required to determine time in minutes, then you can use the km formula and convert hours into minutes.
Here is the formula to calculate time:
Time = Distance / Speed
Let’s look at an example:
How long does it take for a car traveling at 80 km/h to complete a 120-kilometer journey?
Time = 120 km / 80 km/h = 1.5 hours
So, completing that journey will take about 1.5 hours, which is 1 hour and 30 minutes.
What are the real-life applications of this formula?
Well, this formula can be used in nearly every field to determine the time it takes to complete specific tasks. You will have to replace the key variable, which is distance, with what a relevant entity is. For example, if you’re working on how long it takes a machine that produces 30 cups/minute to produce 500 cups, then the variable is 500 cups in this case, while speed is 30 cups per minute.
So, some of the real-life applications of this formula include:
- Commuting: It is used to estimate how long it will take to arrive at a specific destination based on distance and speed. This helps with travel planning.
- Production: This can also be used to calculate the time it takes to produce a specific amount of product based on specific speed and total product
- Sports: Measure how long a race will take based on expected speeds.
How to calculate velocity

Some can’t differentiate between speed and velocity. Velocity is defined to be different from speed because it includes direction also. What makes it different from speed is that it is a vector quantity, which means it has direction as well as magnitude.
The formula for velocity is almost the same as speed, but displacement is used here instead of the total distance, which is the distance in a particular direction.
Here is the formula for velocity:
Velocity = Displacement / Time
What do you notice?
It is similar to a formula for calculating speed, with displacement being the variable entity here.
But first, what is displacement?
Displacement refers to movement in a straight line toward one direction – from the starting point to the endpoint. Unlike speed, where the direction isn’t considered at all, displacement’s primary metric is direction; without direction, then that isn’t displacement.
For example, if you run the trip in a circle, meaning you will end up at the same point, you will have covered X amount of distance while the displacement will be zero. This is because there is no actual displacement, and you’ve ended up at the same point.
Now let’s look at an example:
If it takes a car 2 hours to travel 60 kilometers north, at what velocity was it moving?
Velocity = 60 km north / 2 h = 30 km/h north
This isn’t an ideal example since it is not usually used to solve such problems. Velocity is ideally used to calculate the speed at which a fluid is moving from point A to point B. Other factors also need to be taken into consideration.
How to calculate acceleration
Just like velocity, acceleration is also a vector quantity and depends on content increments of speed, not fluctuating one. This means it involves both magnitude and direction. Acceleration can either be zero, positive or negative, which means:
- Zero: constant speed throughout
- Positive: means it is speeding up
- Negative means it is slowing down, which is also called deceleration.
Here is the formula for acceleration:
Acceleration = (Final Velocity – Initial Velocity) / Time
The SI unit for acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s²).
Here is an example:
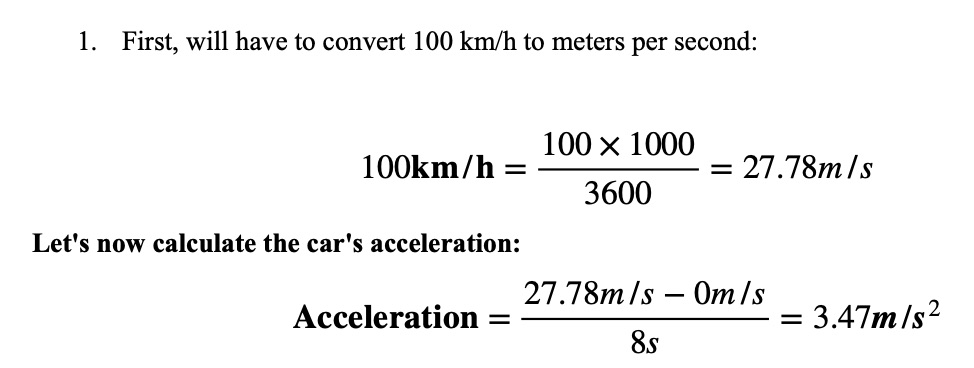
If a car moves from 0 to 100 km/h in 8 seconds, what is its acceleration?
Step-by-step Calculation:
What are the practical uses of acceleration?
Acceleration can be used in various fields as well as in various ways, including
- Vehicle performance: For example, the Tesla Model Y goes from 0-60 mph in 4.80 seconds from rest. This shows how powerful the Tesla Model Y is.
- Physics experiments: Acceleration helps us understand how objects move under various forces, like gravity.
- Engineering: Designing systems like roller coasters or spacecraft, where rapid changes in velocity are common.
How to Calculate Average Speed
At times, you might be traveling from point A to C, but you had to stop at point B for some time before completing. In such scenarios, you will need to calculate average speed, which involves speed from A to B plus speed from B to C.
Average speed provides you with a simple, overall measure of speed for the entire journey regardless of stops.
Formula:
Average Speed = Total Distance / Total Time
Example:
A car travels 100 km in 2 hours, stops for a 30-minute break, and then continues for another 50 km in 1 hour. What is the average speed?
Let’s do the math:
- Total distance = 100 km + 50 km = 150 km.
- Total time = 2 hours + 0.5 hours (break) + 1 hour = 3.5 hours.
- Calculate average speed:
The average speed of the car is 42.86 km/h.
How to Calculate Speed in Circular Motion
When it comes to circular motion, speed is known as tangential speed, which is calculated using an entirely different formula from the speeds and velocity. While the object is constantly changing direction, the speed at any point on the circular path remains the same if the motion is uniform.
Here is the formula to calculate speed in circular motion:

Example:
What is the tangential speed of a satellite orbiting the planet in a circular path with a radius of 10,000 km, completing one revolution every 2 hours?
Let’s do the math:
First, let’s start by converting the radius to meters:
10,000 km = 10,000 x 1000 = 10,000,000 m
Let’s also convert time, which is hours to seconds:
2 hours = 2 x 3600 = 7200 seconds
Now, let’s apply the formula:

From these, we can see that the speed at which the satellite orbits the Earth is 8,726 meters per second.
Related: How to Calculate Average
How to Calculate Speed Using GPS

In addition to the formulas we have mentioned above, you can also utilize GPS to calculate speed.
Today, due to technological developments, speed can be measured with the help of GPS equipment. Global positioning systems determine the speed of the moving object by the signals from the satellite and by finding out the rate of change in the position of the object at a given time interval.
How GPS Measures Speed:
GPS calculates speed by measuring:
- The separation between two places is measured by latitude and longitude.
- The period of time it takes to move from one of those positions to another.
Some of these include GPS devices in smartphones or car GPS navigation systems that have a feature of calculating the speed and displaying it in units of either kilometer per hour (km/h) or miles per hour (mph).
Example:
Speed = 1.5 km / 0.5 hours = 3 km/h
If a GPS device records that a hiker moved 1.5 kilometers in 30 minutes, the speed can be calculated as:
Instantaneous Speed vs. Average Speed
Two related but distinct notions of speed that you need to be aware of are average and instantaneous speed. Average speed refers to the magnitude of the speed over the trip or even over a period of time with stops. On the other hand, the concept of instantaneous speed is somewhat different in that it measures speed at an instant in time.
Instantaneous speed usually requires more advanced equipment like the speedometer in a car or the more detailed information provided by a motion detector.
Example:
Instantaneous speed: This can be considered when you are driving and glance at your speedometer; you feel that the speed of your car is 70 kilometers per hour, and that is your instantaneous speed. But if you go at different speeds during a trip and divide the total time by the total distance, you will have your average speed.
Factors Affecting Speed
The speed of a person or an object can be influenced by several factors that can either be controlled or not. Knowing this is essential as it helps when it comes to practical applications. Knowing these factors can help you determine the ideal way to improve performances and efficiencies, whether as an athlete or designer.
Key Factors:
- Force: Assuming that there is no opposing force, then applying more ore force will lead to greater acceleration and higher speed.
- Friction: friction ideally reduces speed, and so, for instance, friction car tires experienced on the road affects speed.
- Mass: Falling objects primarily utilize their mass to attain the maximum speed possible. However, when it comes to, let’s say, heavier cars, they will require more force to reach higher speeds.
- Air Resistance: The drag or resistance experienced by air can easily affect vehicles, airplanes, and runners.
- Incline/Decline: This is pretty straightforward; moving downhill is effortless and increases speed, while going uphill generally reduces speed due to the need for more force.
Final Thoughts
Measuring speed is among the simplest mathematical operations that are applicable to various fields of life, from transport, games, athletics, or physics to normal daily routine activities.
When you know how to calculate speed, distance, time, velocity, and acceleration, you are able to evaluate motion and performance in different situations. This article provides information on speed in its simplest and most complex forms and is therefore useful for students, engineers, and anyone interested in studying motion.
Whether you are driving a car and need to determine how fast it is going, planning a trip and knowing how long it will take you to get to your destination, or studying physics and learning about acceleration, this guide will help you use speed calculations.